Quality Circles (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + Excel (XLSX) 103 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Provides a framework for the setting up and management of Quality Circles as a channel for employee engagement.
- Provides practical tips to start and sustain Quality Circles in the workplace.
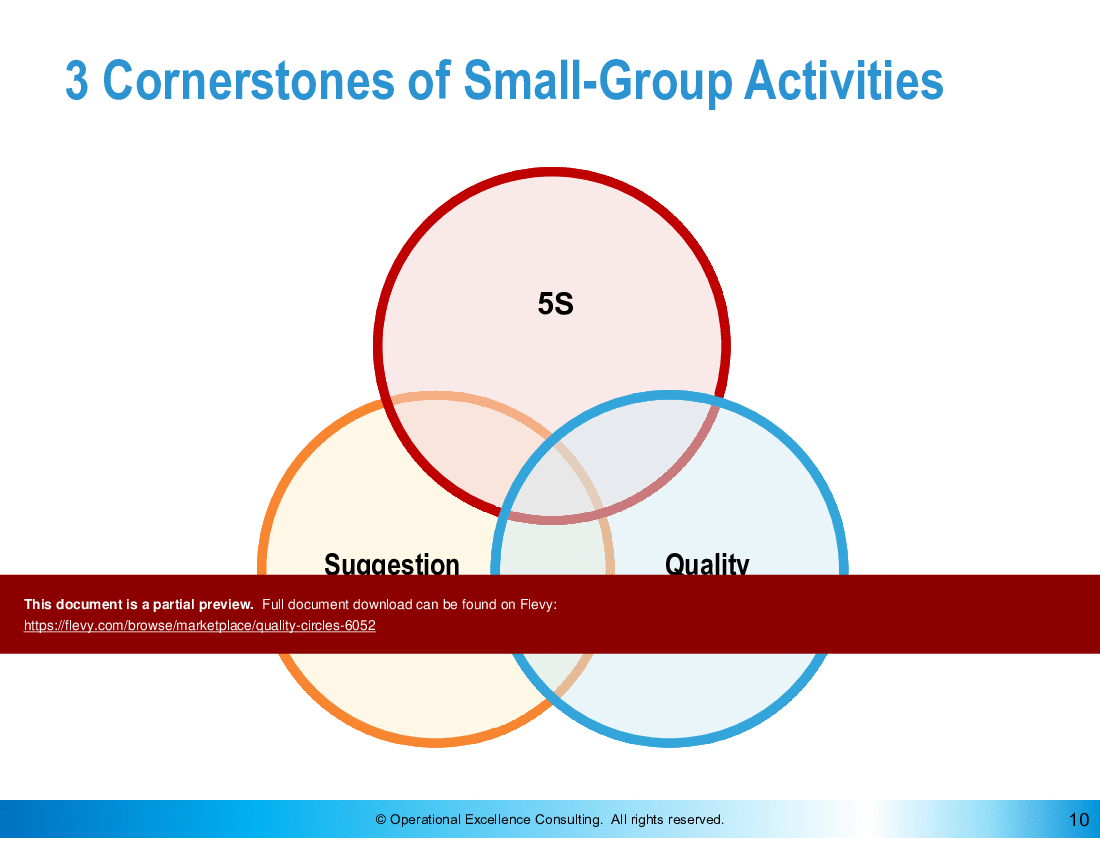
- The Quality Circles framework is applicable to other Small Group Activities such as Kaizen Circles, 5S, TPM, Suggestion System, etc.
QUALITY MANAGEMENT PPT DESCRIPTION
Successful organizations leverage on total employee participation to achieve high quality standards in order to satisfy their customers. However, in the Gallup State of the Global Workplace 2023 Report, only 20% of employees are engaged at work.
As part of the TQM movement, Quality Circles (also popularly known as Quality Control Circles) or Small Group Activities consist of a small group of employees from the same workplace who voluntarily meet on a regular basis to identify, investigate, analyze and solve work-related problems so as to contribute to the improvement of the employees, workgroup and the organization.
The benefits of Quality Circle activities include improved employee morale, reduced absenteeism and staff turnover, improved teamwork and communication, increased productivity, and last but not least improved quality of products and services.
This presentation teaches the philosophy and concept of Quality Circles, defines the objectives, benefits and the modus operandi of Quality Circles. It also describes the organizational structure, roles and responsibilities and provides practical tips for managing Quality Circles. The Quality Circles framework is applicable to other Small-Group Activities such as Kaizen Circles, 5S, TPM, Suggestion System, etc.
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This training package includes:
1. Quality Circles training presentation (PowerPoint format)
2. Forms for administering Quality Circles (Excel formats):
a. Quality Circle Registration Form
b. Approval Form for Theme / Recommendations / Standardization
c. Quality Circle Activity Plan
d. Quality Circle Minutes of Meeting Template
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. Understand the philosophy and concept of Quality Circles.
2. Define the objectives, benefits and the method of Quality Circles operation.
3. Describe the organizational structure and roles and responsibilities of Quality Circles.
4. Gain practical tips for managing Quality Circles and define the key success factors.
CONTENTS
1. Background and Introduction
2. Quality Circles
3. Practical Tips for Managing Quality Circles
4. Overview of PDCA Cycle and QC Tools
5. A Case Study on QC Problem Solving
6. Key Factors for Quality Circle Success
7. Questions for Discussion
Please note that this presentation focuses on the infrastructural set up, formation and management of Quality Circles. It does not include the step-by-step details of PDCA problem-solving process and tools. To complement this presentation with your preferred problem-solving methodology, please check out the various approaches that are available from this author or at Flevy.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 103-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Quality Circles" presentation is a strategic resource designed to enhance employee engagement and problem-solving capabilities within organizations. Developed by Operational Excellence Consulting, this presentation outlines the philosophy, objectives, and practical applications of Quality Circles (QCs), a method that empowers employees to contribute to continuous improvement. By leveraging the insights and tools presented, organizations can foster a culture of collaboration and innovation, ultimately leading to enhanced productivity and quality outcomes.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• HR leaders focused on employee engagement and development
• Operations managers seeking to improve team collaboration and problem-solving
• Quality assurance teams aiming to implement effective quality management practices
• Organizational development professionals interested in fostering a culture of continuous improvement
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During training sessions aimed at introducing Quality Circles to teams
• When launching initiatives to enhance employee involvement in problem-solving
• In workshops focused on continuous improvement methodologies
Learning Objectives
• Understand the philosophy and concept of Quality Circles
• Define the objectives, benefits, and modus operandi of Quality Circles
• Describe the organizational structure and roles and responsibilities of Quality Circles
• Gain practical tips for managing Quality Circles and define the key success factors
Table of Contents
• Background and Introduction (page 6)
• Quality Circles (page 20)
• Practical Tips for Managing Quality Circles (page 32)
• Overview of PDCA Cycle and QC Tools (page 61)
• A Case Study on QC Problem Solving (page 70)
• Key Factors for Quality Circle Success (page 78)
• Questions for Discussion (page 85)
Primary Topics Covered
• Background of Quality Circles - Discusses the evolution of employee engagement and the significance of Quality Circles in enhancing productivity and morale.
• Objectives of Quality Circles - Outlines the goals of QCs, including improved teamwork, employee motivation, and long-term company performance.
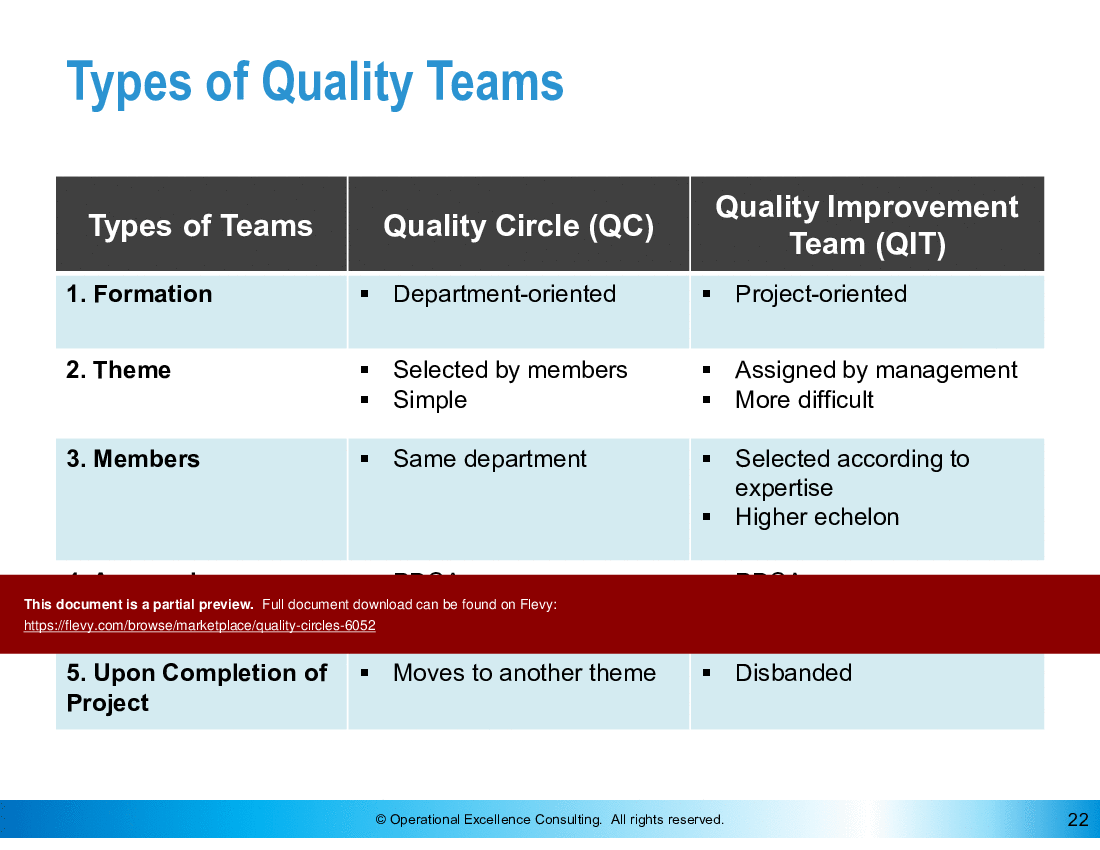
• Structure of Quality Circles - Details the organizational framework for implementing Quality Circles, including roles and responsibilities of team members.
• PDCA Cycle - Introduces the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle as a foundational tool for problem-solving within Quality Circles.
• Case Study on QC Problem Solving - Provides a practical example of how Quality Circles can effectively address and solve workplace issues.
• Key Success Factors - Identifies essential elements for the successful implementation and sustainability of Quality Circles.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Quality Circle registration and activity plan templates
• Meeting minutes and project presentation formats
• Training materials on QC concepts and tools
• Evaluation methods for assessing QC activities
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the PDCA Cycle as a systematic approach to problem-solving
• Case study visuals demonstrating the impact of Quality Circles on reducing scrap in production
• Organizational structure diagram illustrating the roles within Quality Circles
Potential Workshop Agenda
Quality Circle Introduction Session (90 minutes)
• Overview of Quality Circles and their benefits
• Discussion on the philosophy behind employee engagement
Practical Implementation Workshop (120 minutes)
• Hands-on training on PDCA tools and techniques
• Group activities to develop Quality Circle themes and objectives
Evaluation and Feedback Session (60 minutes)
• Review of Quality Circle activities and outcomes
• Discussion on continuous improvement and next steps
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the presentation to reflect specific organizational goals and culture
• Adjust examples and case studies to align with industry-specific challenges
• Incorporate company-specific terminology and metrics for clarity
Secondary Topics Covered
• Employee engagement strategies beyond Quality Circles
• The role of management in supporting Quality Circle initiatives
• Common challenges faced in implementing Quality Circles
Topic FAQ
What are the core components of a Quality Circle program I should plan for?
A Quality Circle program typically includes small employee groups meeting regularly, defined objectives and benefits, an organizational structure with roles (team leader, facilitator, steering committee), problem-solving routines such as PDCA, and templates for registration, activity plans, and meeting minutes as described in the material on organizational structure and roles.How does the PDCA cycle fit into Quality Circles and what level of detail do training packs usually provide?
PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) is presented as the foundational iterative problem-solving framework for Quality Circles; training packs often provide an overview and application examples, but may not include step-by-step PDCA procedures — Flevy's Quality Circles supplies a PDCA overview and related guidance.Which problem-solving tools are commonly used within Quality Circles?
Common Quality Circle tools include root cause analysis techniques such as the 5 Whys and Fishbone (Ishikawa) diagrams, alongside standard PDCA thinking for trial and verification; these specific tools are referenced in the topic coverage and FAQs of the QC material.How should an organization measure the success of Quality Circles?
Success measurement typically tracks improvements in productivity and quality metrics, employee engagement scores, rate of implemented solutions, and related outcomes such as reduced scrap or absenteeism; the materials list these measurement types and evaluation methods tied to QC activities.What should I look for when buying a Quality Circle training and implementation package?
Seek materials that explain QC philosophy and objectives, define structure and roles, provide practical management tips and a case study, and include operational templates (registration, activity plans, minutes) — Flevy's Quality Circles specifically includes PowerPoint training slides plus Excel forms for registration and activity planning.How much workshop time is typically needed to introduce and practice Quality Circles?
A pragmatic introductory agenda in QC materials suggests a 90-minute introduction session, a 120-minute practical implementation workshop for hands-on PDCA exercises, and a 60-minute evaluation and feedback session, matching the sample agendas provided.I need to introduce Quality Circles after a merger—what are the immediate next steps to take?
Immediate steps include tailoring QC materials to new organizational goals and culture, securing management support and resources, running targeted training sessions, establishing roles and governance (steering committee, facilitators), and using standardized forms for registration and activity planning to start pilot circles.Can Quality Circles be applied outside of manufacturing, such as in healthcare or services?
Yes; Quality Circles are adaptable across industries including manufacturing, healthcare, and service sectors, and the presented framework notes applicability to other small-group activities such as Kaizen Circles and 5S, making the approach cross-sector relevant.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What are Quality Circles?
Quality Circles are small groups of employees who meet regularly to discuss and solve work-related problems, enhancing both engagement and productivity.
How can Quality Circles improve employee morale?
By involving employees in decision-making and problem-solving, Quality Circles foster a sense of ownership and pride in their work, leading to higher morale.
What tools are used in Quality Circles?
Common tools include the PDCA cycle, root cause analysis, and various problem-solving techniques such as the 5 Whys and Fishbone diagrams.
How do I measure the success of Quality Circles?
Success can be measured through improvements in productivity, quality metrics, employee engagement scores, and the successful implementation of solutions proposed by the circles.
What support do Quality Circles need from management?
Management support is crucial for providing resources, training, and recognition, as well as fostering an environment conducive to open communication and collaboration.
Can Quality Circles be implemented in any industry?
Yes, Quality Circles can be adapted to various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and service sectors, to improve processes and outcomes.
What challenges might arise when implementing Quality Circles?
Challenges may include resistance to change, lack of management support, insufficient training, and difficulties in maintaining engagement over time.
How often should Quality Circle meetings be held?
Meetings should ideally be held weekly to maintain momentum and ensure continuous progress on identified themes and projects.
Glossary
• Quality Circle (QC) - A group of employees who meet regularly to discuss and solve work-related problems.
• PDCA Cycle - A four-step iterative process used for continuous improvement in quality management.
• Employee Engagement - The level of commitment and involvement an employee has towards their organization and its values.
• Root Cause Analysis - A method of problem-solving that identifies the underlying causes of issues.
• Facilitator - A person who guides and supports the Quality Circle team in their activities.
• Steering Committee - A group responsible for overseeing and supporting Quality Circle initiatives.
• Team Leader - The individual who leads the Quality Circle team and coordinates activities.
• Problem Solving Tools - Techniques used to identify, analyze, and solve problems effectively.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to improve products, services, or processes.
• Employee Involvement - The participation of employees in decision-making processes that affect their work.
• Recognition System - A framework for acknowledging and rewarding employee contributions and achievements.
• Interpersonal Relationships - The connections and interactions between employees in the workplace.
Source: Best Practices in Quality Management PowerPoint Slides: Quality Circles PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, Operational Excellence Consulting
This document is available as part of the following discounted bundle(s):
Save %!
Quality/Kaizen Circle Leader Toolkit
This bundle contains 2 total documents. See all the documents to the right.